Summary
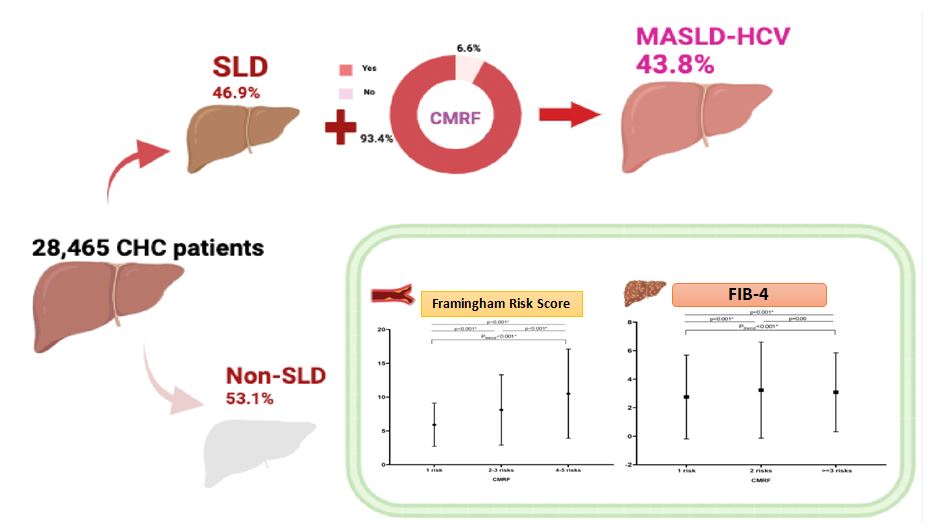
Patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) are prone to develop steatotic liver disease (SLD) and express cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs). The current study aimed to address the liver disease severity of SLD with or without CMRF in chronic hepatitis C (CHC) patients. CHC patients were recruited from a nationwide HCV registry in Taiwan. SLD was defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis on sonography. SLD patients who expressed CMRFs were considered to have HCV metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (HCV-MASLD). A total of 12,462 (93.4%) of the 13,337 SLD patients who expressed at least one CMRF were defined as having HCV-MASLD. The Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4) scores were 2.2±2.1, 2.75±2.94, and 3.13+2.99 in SLD patients without any CMRF, HCV-MASLD patients with only one CMRF and HCV-MASLD patients with> 2 CMRFs, respectively (Ptrend <0.001). Conversely, HCV-MASLD patients with advanced liver disease had a significantly higher Framingham Risk Score than those with a FIB-4 score <2.6 (8.4±5.6 vs. 7.9±5.2, P<0.001). HCV-MASLD patients who expressed one CMRF (odds ratio [OR]/95% confidence intervals [CI]: 1.50/1.22-1.84, P<0.001) or > 2 CMRFs (OR/CI: 1.90/1.57-2.31, P<0.001) were at a greater risk of significant fibrosis than SLD patients without any CMRF. We concluded that CHC patients with SLD and CMRF should be viewed as MASLD as with the general population rather than “miscellaneous SLD”. Attention should be devoted to HCV-MASLD due to the increased risk of advanced fibrosis.
近來歐洲肝臟醫學會和美國肝臟醫學會將脂肪性肝病(steatotic liver disease, SLD)依心血管代謝相關危險因子(cardiometaboic risk factor, CMRF)的有無重新做分類。C型肝炎相關肝臟脂肪化被兩大學會歸類為”其他類脂肪性肝病(miscellaneous steatotic liver disease)”。本研究的目的在於釐清C型肝炎患者相關肝臟脂肪化及心血管代謝相關危險因子的比例,以及其對肝臟纖維化及心血管風險的影響,進而審視其是否應歸類為”代謝異常相關脂肪性肝病(metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; MASLD)”。本計畫針對台灣多中心一共收錄13,337位C肝SLD患者,其中高達93.4%的病人具有至少一個CMRF。其中肝纖維化的分數Fibrosis-4 Index (FIB-4)及心血管風險係數Framingham Risk Score隨著 CMRF的有無及數目成正相關。比較起未帶有CMRF的SLD患者,帶有一個及兩個以上CMRF的患者其具有進展性肝纖維化的風險分別為1.5倍及1.9倍。綜上,C型肝炎SLD患者具有高CMRF的特性,及其與肝臟纖維化程度及心血管風險具有高度相關。此些特性歸納起來與過往脂肪肝研究一般患者相似。因此C肝相關SLD 不應僅是某些學會定義的miscellaneous steatotic liver disease,,若其具備CMRF更可歸類為”MASLD-HCV”。